Overview
Since November 2022, I have primarily participated in the following research projects:
Range-Direction Beamforming for Wireless Power Transfer
Cylindrical Array Design to Optimize Polar-Azimuthal Direction-Finding Resolution
How an Acoustic Velocity-Sensor’s Direction-Finding Precision is Affected by Angular Spreading of the Incident Source
1. Range-Direction Beamforming for Wireless Power Transfer Project
We focus on one specific attenna, Frequency diverse array (FDA), which
- Synthesis of a beam pattern that has resolution over range and direction.
- With frequency offset at each antenna of the array.
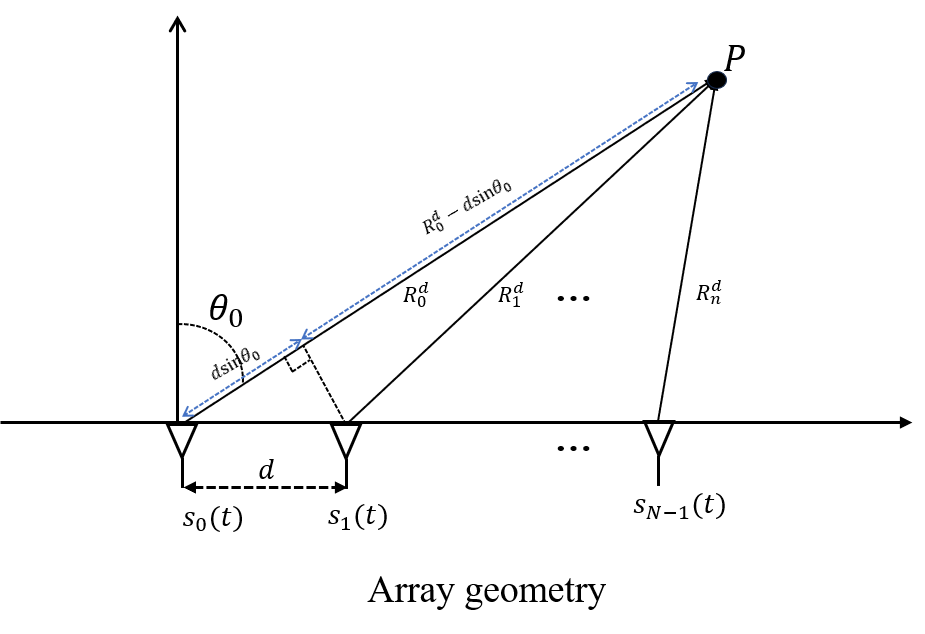
Assume $N$ attennas employed,
The signal of the $n$-th antenna is given by: $s_n(t) = b_n^* e^{j2\pi f_n t} w(0, T)$
The frequency of the $n$-th antenna is: $f_n := f_c + \Delta_{f_n}^{(f)}, \quad \forall n = 0, 1, \ldots, N-1$
where $b_n$ and $\Delta_{f_n}^{(f)}$ are the $n$-th attenna’s weight and frequecy-offset, and their values are not presetted.
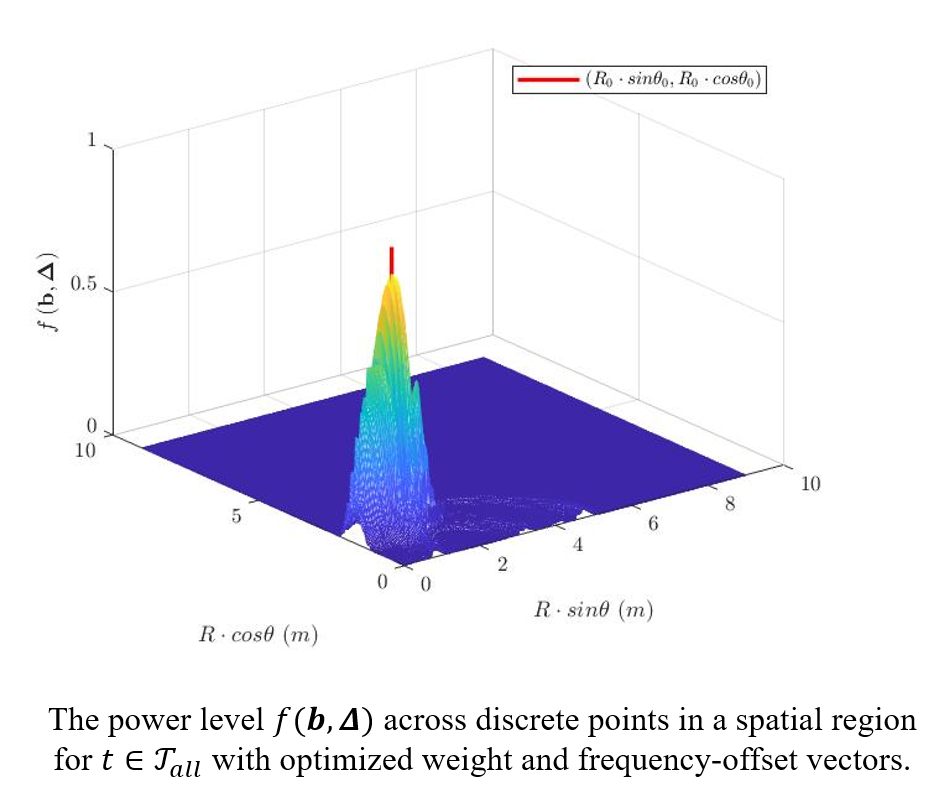
Our objective is to optimize the antennas’ weights and frequency-offsets for efficient wireless power transfer to a specific position. This optimization is particularly beneficial for near-field wireless power transfer applications, such as smartphone charging.
My work includes the following:
- Specifying various cost functions and constraints and formulating the optimization problems in detail, based on different ideas provided by my advising professors.
- Simultaneously optimize $b_n$ and $\Delta_{f_n}^{(f)}$ using Matlab solvers such as
fmincon,ga(genetic algorithm), etc.
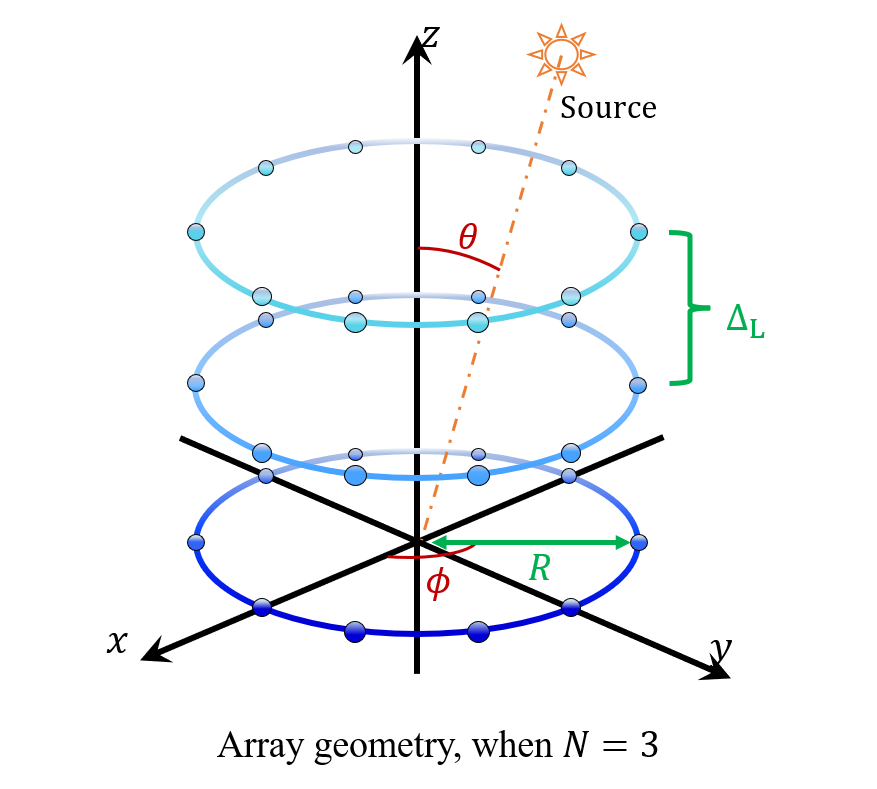
2. Cylindrical Array Design to Optimize Polar-Azimuthal Direction-Finding Resolution Project
This project proposes a closed-form design procedure for cylindrical uniform sensor arrays by analyzing the trade-off between array volume and the measurement accuracy of azimuthal angles($\phi$) and polar angles($\theta$). Specifically, we aim to specify the parametric values of${N, \Delta_{L}, R}$ to satisfy following criteria:
(A) Achieving higher resolution for the source signal, which is reflected in lower values of the Cramer-Rao Bound (CRB), including the CRB for the incident polar and azimuthal angles.
(B) Ensuring ease of application by occupying a smaller volume and surface area, making it more convenient for deployment.
My work includes the following:
- Deriving the Cramer-Rao Bound from the array manifold.
- Proposing a closed-form design procedure.
- Creating graphs, writing in LaTeX, and performing other related tasks.
3. How an Acoustic Velocity-Sensor’s Direction-Finding Precision is Affected by Angular Spreading of the Incident Source Project
This project primarily investigated the impact of incident source angle deviation on direction-finding accuracy for 2 or 3 superimposed figure-8 sensors and(or without) a pressure sensor under different placement methods.
Two sub-projects are consisted in this project, corresponds to two different different placement methods of sensors respectively:
a) How a Bi-Axial Velocity-Sensor’s Direction-Finding Precision is Affected by Angular Spreading of the Incident Source
b) How a Tri-Axial Velocity-Sensor’s Direction-Finding Precision is Affected by Angular Spreading of the Incident Source
In the above two sub-projects, my work includes the following:
- Deriving the Fisher Information Matrix and Cramer-Rao bound from the array manifold, with respect to the known/unknown variance of elevation and azimuth angles a priori.
- Analyzing and explaining the trend of the Cramer-Rao bound with varying variance of noise, elevation angle, etc.
- Creating graphs, writing in LaTeX, and performing other related tasks.
